Registering a servlet
Create a servlet class
To create a servlet class, extend javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet. Most
servlets extend this class.
HttpServlet
provides an abstract class to be subclassed to create an HTTP servlet
suitable for a website. A subclass of HttpServlet must override at
least one method, usually one of these:
-
doGetfor HTTPGETrequests -
doPostfor HTTPPOSTrequests -
doPutfor HTTPPUTrequests -
doDeletefor HTTPDELETErequests -
initanddestroyto manage resources that are held for the life of the servlet -
getServletInfofor the servlet to provide information about itself
There’s almost no reason to override the service method, which
handles standard HTTP requests by dispatching them to the handler
methods for each HTTP request type (the do methods listed above).
Likewise, there’s almost no reason to override the doOptions and
doTrace methods.
Servlets typically run on multithreaded servers, so be aware that a servlet must handle concurrent requests and be careful to synchronize access to shared resources. Shared resources include in-memory data such as instance or class variables and external objects such as files, database connections and network connections.
Additionally, implement info.magnolia.cms.filters.SelfMappingServlet. This is an optional interface that servlets wrapped by info.magnolia.cms.filters.ServletDispatchingFilter can implement to provide their own mapping. When implementing this method, the servlet can get the mapping from any arbitrary component. This means the mapping can be configured centrally and reused by other components, typically to generate links. See Dynamic servlet mapping for more information.
Define the servlet in your module descriptor
Define the servlet in your module
descriptor. Include any mappings and init parameters the servlet class
supports.
- Example
-
The Magnolia Core module descriptor (
core.xml) registers the info.magnolia.cms.servlets.ClasspathSpool servlet. The purpose of this servlet is to serve resource files such as CSS and JavaScript from themgnl-resourcesfolder of any module when requested with the path/.resources/<module name>.
<servlets>
<servlet>
<name>ClasspathSpoolServlet</name>
<class>info.magnolia.cms.servlets.ClasspathSpool</class>
<comment>Used to serve resources from the classpath.</comment>
<mappings>
<mapping>/.resources/*</mapping>
</mappings>
</servlet>
</servlets>Initialization parameters:
-
name: name of the servlet -
class: fully qualified name of the servlet class -
comment: description of what the servlet does -
mappings: URLs and paths that direct requests to the servlet
You don’t need to add the servlet to your
web.xml.
|
- Examples
Configure the servlet in the filter chain
Configure the servlet in the
filter chain
in Configuration > /server/filters/servlets. The
configuration is created automatically when the module is installed. The
values are taken from the module descriptor.
Servlets are registered by
info.magnolia.module.delta.RegisterModuleServletsTask at
install time. This means that if the definition changes over time, the
module developer should update the configuration by using
ModuleVersionHandler.
|
- Example
-
ClasspathSpoolServletis configured in/server/filters/servlets/ClasspathSpoolServlet. The default/mgnl-resourcesis hard-coded but can be configured with theresourcesRootinitparameter. The servlet loads files from this folder and makes them available in the path defined in thepatternparameter.
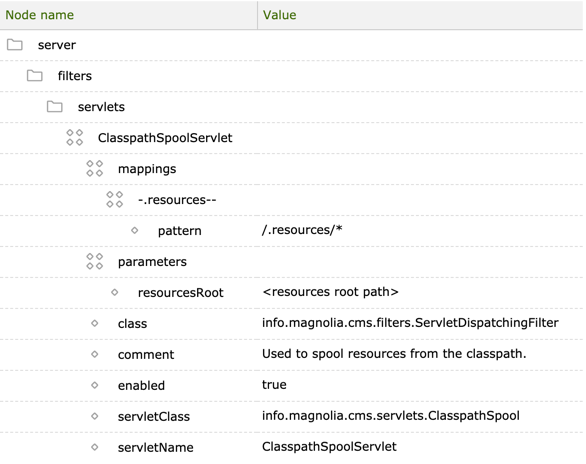
Properties:
-
<servlet name>: name of the servlet as defined in theservletNameproperty-
mappings: URLs and paths that direct requests to the servlet-
<mapping name>-
pattern: URL pattern that triggers the servlet
-
-
-
parameters: parameters supported by the servlet class-
<parameter name>
-
-
class: filter class. All servlets use theinfo.magnolia.cms.filters.ServletDispatchingFilterclass, which dispatches requests to a wrapped servlet. The filter initializes the servlet and its mappings.ServletConfigis wrapped to takeinitparameters into account. -
comment: servlet description -
enabled: enables and disables the servlet. The default value istrue. -
servletClass: fully qualified name of the servlet class -
servletName: name of the servlet as defined in the module descriptor
-