Users
A user is an account that identifies the person accessing Magnolia. In addition to a username, Magnolia stores the user preferences such as full name, email address, language, and time zone. These settings can be edited by the users themselves.
Every user has a certain set of permissions to grant access to resources, content, apps, and so on. Users inherit their permissions from the groups and roles they’re attached to (see Organizing users). Use the Security app to edit the permissions of a user.
Types of users
| Type | Example | Security app folder | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Users |
Accounts for people who work on site content such as authors, editors, and publishers. |
|
|
System users |
Technical accounts such as |
|
|
Public users |
End users or visitors of the site. They can be registered through the Public User Registration (PUR) module. Registering visitors allows you to provide them with personalized content such as members-only sections of the site, newsletters, and mailing lists. |
|
superuser user
The term superuser may refer either to a system user (an account type) or to a role (a definition of what a user is allowed to do in the system).
In a typical installation of Magnolia, the superuser role is assigned to the superuser account.
In addition to the superuser role, the superuser account has some other roles too (see Default roles, groups and users).
As the name implies, the permissions of the superuser account are usually unrestricted in any way.
For instance, superuser can read and write to all default JCR workspaces on /.
On a production system, create specific users with distinct roles and deactivate the superuser account.
anonymous user
The term anonymous may refer either to a system user or to a role.
The latter is assigned to the former.
Apart from the anonymous role, the anonymous system user is by default assigned other roles too (see Default roles, groups and users).
Every Magnolia resource intended to be accessible without authentication must be enabled for the anonymous system user. A users that interacts with Magnolia without authentication is determined as an anonymous user.
|
On most systems, the rights and permissions of the anonymous role differ between author and public instances: allow read access to all on the public instance, while denying the same on the author instance. That’s why you should not activate this role. |
Organizing users
In Magnolia, users are organized as follows:
-
Users can have both roles and groups.
-
Groups can have groups and roles.
-
Roles can have only Access Control Lists (ACLs).
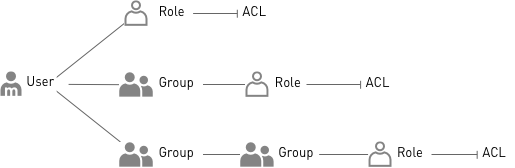
Permissions are defined in the ACLs. Users inherit permissions from the roles and groups assigned to them.
In a small site you can manage users and groups in Magnolia. On a larger site (hundreds of users), it’s better to manage users and groups in an enterprise-grade user management infrastructure, such as Microsoft Active Directory. You would define roles and ACLs in Magnolia but manage users and groups in the external system.
| Get a list of all permissions assigned to a user or group in the Tools tab of the Security app. |
Editing user permissions
Every user known to Magnolia is granted a set of permissions defined by roles. You can either assign roles directly to a user, or assign a user to a group that itself grants a set of roles (see Organizing users above).
Use the Security app to edit the permissions.
The app is available in the Set up group of AdminCentral, and by default the superuser role is required to access it.

The Security app provides subapps to edit the users (system users and public users), groups, and roles. Select the user you want to edit and double-click it or use the Edit user action. The Edit user action is available in the following subapps: Users, System users and Public users.

The dialog where you can edit user details has three tabs:
-
User info: Edit the user’s name and full name, the password, the email address, and the language. The language can also be edited in the Edit user profile dialog. You can use the tab to enable or disable a user account.

-
Groups: Assign the user to existing groups.

-
Roles: Grant roles to the user.

Automatic lockout
An automatic lockout is a security precaution that prevents users from accessing Magnolia after a number of failed login attempts.
By default, a lockout is triggered and an account is automatically disabled after N+1 failed login attempts.
The number of failed attempts can be configured.
No lockout is triggered when a username that doesn’t exist is entered.
A lockout applies to both system and admin users, but not to public users.
After a lockout, an administrator can re-enable the account by selecting the Enabled checkbox in the user profile.
When a lockout occurs, this checkbox is cleared.

The number of failed login attempts N that will trigger a lockout can be configured using the maxFailedLoginAttempts property in /server/security/userManagers/system and /admin.
Different values may be set for Users and System Users.
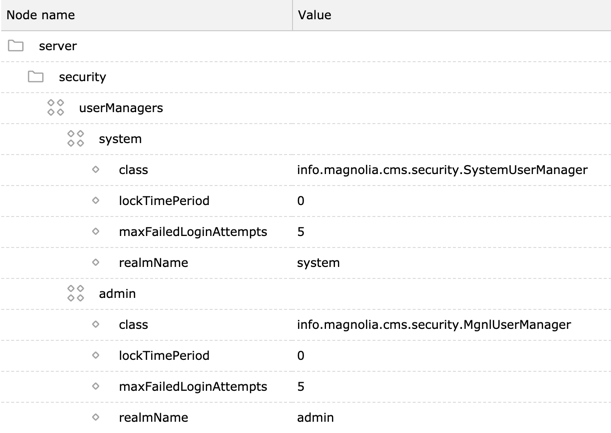
Properties
| Property | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
optional, default is Allows duplicate usernames in different realms. Only applicable to |
||
|
required A class that implements the info.magnolia.cms.security.UserManager interface. Implementations:
|
||
|
optional, default is Allows to disable caching if set to |
||
|
required Realm name corresponding to JAAS login configuration. |
||
|
optional, default is Indicates what methods are used to deal with the
|
||
|
optional A subnode that allows you to specify a custom |
||
|
The class that implements the The default class used is Two additional implementations are available:
|
||
|
optional A subnode that specifies the If not defined explicitly, then the predicate accepts anything within the following namespaces:
|
||
|
The class that implements the The default class is |
||
|
optional A subnode that defines the decoding method of the admin password used by the
|
||
|
The decoder is available in three implementations:
|
||
|
optional, default is Specifies the number of objects to be returned in a single search result. |
External services
The LDAP Connector module is a standard JAAS login module that connects to any LDAP V3 supported directory service. This module is useful where an enterprise-grade user management infrastructure already exists. With the JAAS standard support, you can meet single sign-on requirements or connect to legacy LDAP/ADS directory servers.