GraphQL module
Multi-experience support Bundled: DX Core
| Edition | DX Core |
|---|---|
License |
|
Issues |
|
Maven site |
|
Latest |
1.1.11 |
The GraphQL module allows you to expose content stored in JCR through GraphQL POST and GET requests. The module provides a GraphQL API, a binding to Magnolia assets and a seamless integration with content types.
Module structure
| artifactID | |
|---|---|
|
Parent reactor. |
|
Integrates GraphQL with Magnolia assets. |
|
Provides the API. |
|
Integrates GraphQL with Magnolia content types and JCR. |
Installing with Maven
Bundled modules are automatically installed for you.
If the module is unbundled, add the following to your bundle including your project’s <dependencyManagement> section and your webapp’s <dependencies> section.
If the module is unbundled but the parent POM manages the version, add the following to your webapp’s <dependencies> section.
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.graphql</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-graphql-core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.11</version> (1)
</dependency>| 1 | Should you need to specify the module version, do it using <version>. |
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.graphql</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-graphql-jcr</artifactId>
<version>1.1.11</version> (1)
</dependency>| 1 | Should you need to specify the module version, do it using <version>. |
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.graphql</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-graphql-assets</artifactId>
<version>1.1.11</version> (1)
</dependency>| 1 | Should you need to specify the module version, do it using <version>. |
Bundled with magnolia-dx-core-demo-webapp
From Magnolia 6.2.10, the module is bundled with magnolia-dx-core-demo-webapp.
You can download the webapp from the release notes or files.magnolia-cms.com.
Configuration
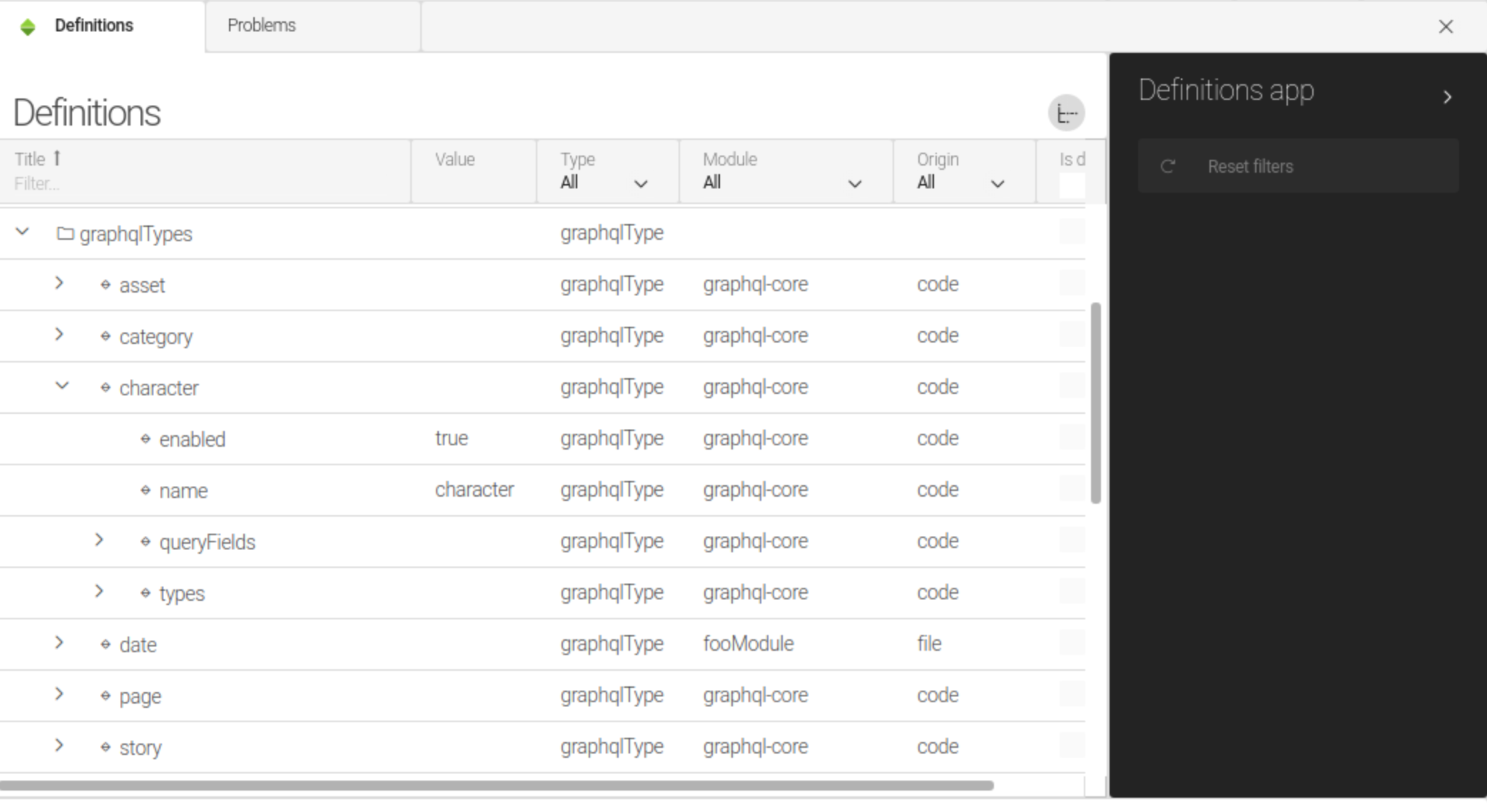
The module itself does not require any configuration adjustments. It is ready for use once your Magnolia instance is up and running. Registered GraphQL types can be verified using the Definitions app:
Disabling specific GraphQL types
If you need to disable a GraphQL schema for a content type, you can do so through definition decoration, for example:
/your-module/decorations/graphql-core/graphqlTypes/character.yaml
enabled=falseDisabling GraphQL servlet
By default, the GraphQL servlet is enabled. To disable it, set the /server/filters/servlets/GraphQLServlet@enabled property to false.
Changing endpoint name
By default, all GraphQL requests are mapped to /.graphql. You can change this by modifying the pattern property at /server/filters/servlets/GraphQLServlet/mappings/-.graphql--.
GraphiQL servlet
The magnolia-graphql-core module installs GraphiQL, a servlet which you can use to explore the GraphQL API and test your GraphQL requests.
The servlet is exposed in two forms:
-
As the GraphQL app, available in the Dev group of the App launcher.
-
Directly in your web browser. On a localhost installation of Magnolia, the URL to access the servlet is
http://localhost:8080/magnoliaAuthor/.graphiql.
Servlet configuration
The servlet is installed as GraphiQLServlet under /server/filters/servlets/.
Its default configuration can be modified under /modules/graphql-core/config/graphiql/ using the following properties.
Base properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
optional, default is GraphQL endpoint servlet mapping. The value must correspond with the value of the |
|
optional, default is Path to the GraphiQL FreeMarker file. If needed, |
CDN-related properties
These properties must be configured under /modules/graphql-core/config/graphiql/cdn/.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
optional, default is If |
|
optional, default is GraphiQL version to serve from a CDN. |
Security
Access control
All requests to the GraphQL servlet pass through a filter chain. Make sure that the instance handling GraphQL requests in a production environment has an appropriate assignment of JCR Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Web Access permissions for the GraphQL endpoint and for the JCR workspaces where GraphQL content is stored. For more information, see the Security app.
Query limits
GraphQL module 1.1.11 and later provides built-in protection against denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
These mechanisms enforce strict limits on query complexity and nesting depth.
Why query limits matter
GraphQL’s flexibility allows clients to construct arbitrarily complex queries. Without limits, a malicious client could exploit this through:
-
Field duplication: Requesting the same field hundreds of times to exhaust server resources.
-
Deep nesting: Constructing deeply nested queries that consume excessive memory and CPU.
-
Alias overloading: Using aliases to bypass naive field counting and execute expensive operations repeatedly.
The module enforces limits to mitigate these specific attack vectors.
Query limits configuration
You can configure query limits in the module configuration at /modules/graphql-core/config.
📁 modules |
|
📁 graphql-core |
|
📁 config |
|
⬩ maxQueryDepth |
15 |
⬩ maxQueryComplexity |
200 |
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
optional, default is The maximum nesting depth allowed in a query.
The minimum value is |
|
optional, default is The maximum total field count allowed (including duplicates and aliases).
The minimum value is |
Any changes to maxQueryDepth and maxQueryComplexity require a server restart to take effect.
|
How complexity is calculated
Every field requested in a query contributes 1 point to the total complexity.
This calculation includes:
-
Duplicate fields (requesting the same field multiple times).
-
Aliased fields (each alias counts as a distinct field).
-
Nested fields (costs are cumulative).
-
Fragment spreads (fields within fragments are expanded and counted).
-
Inline fragments (every field within an inline fragment counts).
{
page { # 1
title # 1
title # 1 (duplicate counts!)
content # 1
children { # 1
title # 1
}
}
}
# Total complexity: 6Error responses
When a request fails due to these limits, the module returns an appropriate HTTP status code accompanied by a sanitized error message:
| Condition | HTTP code | Error message |
|---|---|---|
Query complexity/depth exceeded |
|
|
GraphQL validation error |
|
|
Invalid request format (e.g., array instead of object) |
|
|
Malformed JSON |
|
|
Introspection disabled |
|
|
Item not found |
|
|
Internal server error |
|
|
{
"status": 400,
"errors": ["Query exceeds allowed limits."]
}For security reasons, the specific limit values are not exposed in client-facing error messages.
Detailed information regarding the rejection is logged server-side at the WARN level.
Adapting to the new limits (existing integrations)
Most legitimate queries continue to function without modification. The default limits are calibrated to accommodate standard usage:
-
A complexity of
200covers typical content queries. -
A depth of
15exceeds the requirements of most content models.
If your queries are being blocked:
-
Check server logs to identify the specific limit exceeded and review query details.
-
Simplify queries using the following strategies:
-
Remove duplicate field requests.
-
Reduce nesting depth.
-
Split massive queries into smaller, specific requests.
-
-
Adjust limits only if your use case legitimately demands higher values.
# Example: Allow more complex queries for admin tools
maxQueryComplexity: 500
maxQueryDepth: 20
Standard introspection queries (typically ~109 fields) fit well within the default complexity limit of 200.
|
Monitoring
The system logs rejected queries at the WARN level:
WARN GraphQL query rejected: complexity exceeded. Query: {query...}
WARN GraphQL query rejected: depth exceeded. Query: {query...}Monitor these logs to identify:
-
Potential malicious attack attempts.
-
Legitimate queries that require configuration adjustments.
-
Integration issues arising after the upgrade.
Technical details
-
Defense layers
The module implements a two-layered protection strategy:
-
Depth instrumentation: Rejects queries before execution if nesting exceeds
maxQueryDepth. -
Complexity instrumentation: Rejects queries before execution if the total field count exceeds
maxQueryComplexity.Both checks occur before query execution, ensuring that rejected queries do not consume database or JCR resources.
-
-
Fragment handling
GraphQL fragments are fully expanded prior to complexity calculation. This approach prevents bypass attempts that rely on fragment duplication:
# This query has complexity 25 (5 fields × 5 spreads), not 5 fragment F on Asset { name name name name name } query { asset(id: "1") { ...F ...F ...F ...F ...F } } -
Error sanitization
-
All error messages undergo sanitization before transmission to clients.
-
Detailed error information, including actual limit values and full query text, is logged server-side only to prevent information leakage to potential attackers.
-
Usage
-
See GraphQL API.