DAM API
The DAM API abstracts the storage location of assets, allowing you to work with assets regardless of where they are stored. You use the API in templating, templates, and models. It provides read-only access to assets managed in the Magnolia Assets subapp.
The DAM API provides the following features:
-
Clean, simple, and easy to use.
-
Flexible, extendable, and user-friendly. You can extend the API and create your own asset providers for external systems.
-
Generic and not tied to JCR.
-
Connects to external asset providers such as Flickr, YouTube, and file systems.
-
Supports industry-standard media types.
-
Separates asset metadata from binaries.
Architecture
The diagram provides an overview of how the main interfaces and classes of the DAM API relate.
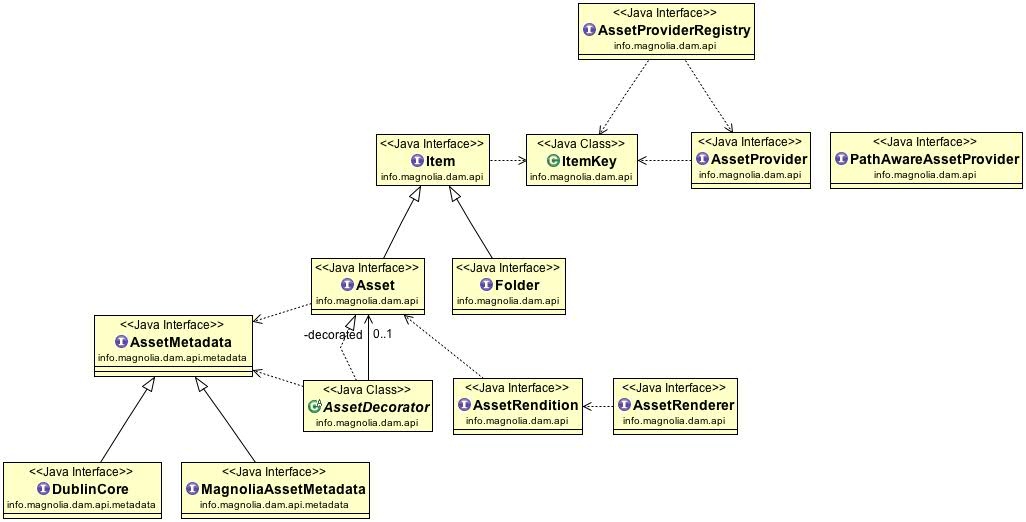
Interfaces
-
info.magnolia.dam.api.AssetProviderRegistry is the main entry point. Given an
ItemKeyorMediaType, it’s responsible for finding the correctAssetProviderandAssetRenderer. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.AssetProvider: Exposes
FoldersandAssetsfrom a particular source. Specifics of the storage of these items are left to implementations. While most provider implementations only use theItemKey.assetIdfield of keys passed to the variousgetmethods, the entire key object is passed for consistency and flexibility. This makes it possible to implement, for example, delegating and aggregating providers. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.PathAwareAssetProvider: Exposes specific operations for
AssetProvidersthat are aware of paths, for example JCR, CMIS, File system etc. Not all providers need or want to implement these features. The term "path" is flexible. It can represent a single name or a relative path within the data source. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.AssetRenderer: Provides
AssetRenditionsby bridging an asset’s data and some type of converter.AssetRendererscan be provided byAssetProvidersif theAssetProvideritself (or the underlying system) is capable of managing the conversion/translation, or via aglobalregistry.AssetProviderRegistry.getRendererFor(info.magnolia.dam.api.Asset, com.google.common.net.MediaType)provides the entry point. It looks up in provider, then in its own registry, and bridges to other possible conversion mechanisms that are independent of Magnolia DAM. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.Asset: An
Assetis a digital resource with associated metadata. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.Folder: A
Folderrepresents a structural item holdingAssets. Depending on the provider, this can be directly mapped to the concept of folders/directories (JCR, FileSystems and so on), and for other types, it may map to the concept of albums,playlists, sets, and so on. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.Item: Defines a common interface for
AssetandFolder. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.AssetQuery: Represents a query to an
AssetProvider. Use newAssetQuery.Builder()…build()to construct instances. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.AssetRendition: An
AssetRenditionis aviewon a asset for a specificMediaType. It can be a simple resize of an image or a document conversion.
Enum
-
info.magnolia.dam.api.AssetProviderCapability: Clients can ask a provider if they support a certain feature before attempting to use it. Typically, this would enable or disable certain UI features. In some cases, this also indicates that client code can cast to a specific interface (such as
PathAwareAssetProviderforhierarchical). If support for write operations is added, this enum is extended with new capabilities.
Classes
-
info.magnolia.dam.api.AbstractAssetProvider: Convenient abstract base class for implementations. Enables configurations of
MediaTypethat the implementedAssetProviderprovides. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.AbstractItem: Common superclass for any DAM
Item. -
Builder: A builder forAssetQuerythat provides a fluent API. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.ItemKey: A composite key. In the DAM, every
AssetandFolderis identified by its provider’s ID and its provider-specific ID (that is, the ID with which the provider can uniquely identify the asset).
Metadata interfaces
-
info.magnolia.dam.api.metadata.AssetMetadata: A common interface for asset metadata. Different types of metadata can be exposed through
Assetby extending this interface. TheAssetProvidershould implement support for those. Specific metadata interfaces should expose methods with explicit names and return types, and ideally provide property descriptions in the Javadocs. Metadata is retrieved through anAssetby passing the specific type of metadata, that is, a class object that extends this interface. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.metadata.DublinCore: A collection of Dublin Core metadata names. Extends
AssetMetadata. Methods:getContributor,getCoverage,getCreated,getCreator,getDate,getDescription,getFormat,getIdentifier,getLanguage,getModified,getPublisher,getRelation,getRights,getSource,getSubject,getTitle,getType. -
info.magnolia.dam.api.metadata.MagnoliaAssetMetadata: Defines Magnolia-specific metadata. Extends
AssetMetadata. Methods:getHeight,getWidth.
Asset binary management
In DAM 5 and later, Magnolia deprecates Asset.getContentStream in favor of Asset.getBinaryReference.
This decouples asset binaries from Magnolia, making it easier to retrieve binaries outside the Magnolia instance.
The magnolia-dam-binary-api module provides interfaces for binary management without dependencies on Magnolia modules.
You can implement your own binary management solution with minimal effort.
import info.magnolia.dam.binary.api.BinaryGetter;
import info.magnolia.dam.binary.api.BinaryReference;
import info.magnolia.dam.binary.api.Binary;
public class MyClass {
@Inject
public MyClass(BinaryGetter binaryGetter) {
this.binaryGetter = binaryGetter;
}
public Optional<InputStream> binaryFromReference(BinaryReference binaryReference) {
return binaryGetter.getBinary(binaryReference)
.map(Binary::getInputStream);
}
}AssetProvider
-
AssetProviderhascapabilities(info.magnolia.dam.api.AssetProviderCapability). Some implementations will not support all features. This can be used to drive a UI to enable/disable certain actions or UI elements. Implementations should still throw exceptions when those unsupported operations are called. However, this may not consistently be the case, for example when aggregating search results from different providers. -
ItemKeyis a specific type (composed ofproviderIdandassetId) rather than amagic string. It’s passed to most methods, rather than theassetIdstring. This allows for aggregation/delegation in specialized providers.
AssetProviders are registered by configuration in the DAM Core module.
Items, assets and folders
-
Itemis the main parent definition of aFolderand anAsset. -
Assetis the abstract representation of a binary document. -
Folderis the abstract representation of a folder that containsAsset.
AssetRenditions and MediaTypes
An AssetRendition is a transformation of an Asset.
The AssetRenderer provides AssetRenditions by bridging an Assets dataand some type of converter.
-
AssetRenderercan be provided byAssetProviderwhen the conversion or translation can be managed by theAssetProvideritself (or its underlying system), or via aglobalregistry. -
`AssetProviderRegistry.getRendererFor(Asset asset,MediaType mediaType)`provides the entry point. It looks up in the provider then in its own registry, and bridges to other possible conversion mechanisms that are independent of the Magnolia DAM.
AssetRenderers are registered by configuration in the DAM Core module.
MediaType
In DAM 2.0 and later, the com.google.common.net.MediaType class is included in the Google Guava library.
Here’s the class description from the Guava Javadoc.
Represents an Internet Media Type (also known as a MIME Type or Content Type). This class also supports the concept of media ranges defined by HTTP/1.1. As such, the
character is treated as a wildcard and is used to represent any acceptable type or subtype value. A media type may not have wildcard type with a declared subtype. Thecharacter has no special meaning as part of a parameter. All values for type, subtype, parameter attributes or parameter values must be valid according to RFCs 2045 and 2046.All portions of the media type that are case-insensitive (type, subtype, parameter attributes) are normalized to lowercase. The value of the
charsetparameter is normalized to lowercase, but all others are left as-is.Note that this specifically does not represent the value of the MIME
Content-Typeheader and as such has no support for header-specific considerations such as line folding and comments.For media types that take a charset the predefined constants default to UTF-8 and have a
_UTF_8suffix. To get a version without a character set, usewithoutParameters().
JCR API
The DAM JCR API classes reside in the DAM JCR module and implement the DAM API for JCR assets that are stored in the dam workspace and accessible in the Assets app.
| In DAM 5 and later, the JCR API implementation changes to allow binaries to be stored outside of JCR. This means you may experience compatibility issues when upgrading from previous versions. We don’t recommend using the JCR API for any new development; use the DAM API instead. |
JCR classes
-
info.magnolia.dam.jcr.JcrAssetProvider:
AssetProviderthat delivers assets for thedamworkspace. ExtendsAbstractAssetProviderand implementsPathAwareAssetProvider. -
info.magnolia.dam.jcr.AbstractJcrItem: JCR implementation of an
Item. ExtendsAbstractItem<JcrAssetProvider>. -
info.magnolia.dam.jcr.JcrAsset: JCR implementation of the
Assetdefinition. ExtendsAbstractJcrItem. -
info.magnolia.dam.jcr.JcrFolder: JCR implementation of the
Folderdefinition. ExtendsAbstractJcrItem. -
info.magnolia.dam.jcr.AssetNodeTypes: Constants and convenience methods for asset node types.
-
Asset: Represents the node typemgnl:asset. Fields:caption,comment,copyright,description,language,master,name,provider_type,subject,title,type. -
AssetResource: Represents the resource node bound to anAsset. Fields:data,extension,filename,height,mimetype,name,ressource_name,size,width.
-
-
info.magnolia.dam.jcr.JcrItemNodeTypePredicate: Predicate filtering asset nodes (folders and assets) based on the following
Node.getPrimaryNodeType():-
AssetNodeTypes.Asset.NAME -
NodeTypes.Folder.NAME
-
Extends info.magnolia.jcr.predicate.AbstractPredicate<jakarta.jcr.Node>.
-
info.magnolia.dam.jcr.DamConstants: Defines commonly used constants for the DAM JCR module. Fields:
default_jcr_provider_id,workspace.
Custom JCR asset properties
In order to access a custom property defined under a JCR Asset node, info.magnolia.dam.jcr.JcrAsset provides a public getter:
/**
* JcrAsset specific implementation that lets you access a property value linked to an asset node.
* This requires an open session.
*
* @return property value Object if the property exists or null otherwise.
*/
public Object getProperty(String propertyName) {
return PropertyUtil.getPropertyValueObject(getNode(), propertyName);
}JCR metadata classes
-
info.magnolia.dam.jcr.metadata.JcrDublinCore: JCR implementation of
DublinCore. Fields:dc_contributor,dc_coverage,dc_creator,dc_publisher,dc_relation,dc_source,dc_subject,dc_type. Methods:getContributor,getCoverage,getCreated,getCreator,getDate,getDescription,getFormat,getIdentifier,getLanguage,getModified,getPublisher,getRelation,getRights,getSource,getSubject,getTitle,getType. -
info.magnolia.dam.jcr.metadata.JcrMagnoliaAssetMetadata: Base JCR implementation of the
MagnoliaAssetMetadatadefinition. Methods:getHeight,getWidth.
Accessing the DAM API
To access AssetProviderRegistry from your custom module, adapt your pom and module descriptor XML files to include a dependency.
You can simply inject or use components to access AssetProviderRegistry.
private final AssetProviderRegistry providerRegistry;
// By Injection
@Inject
public MyFunctions(AssetProviderRegistry providerRegistry) {
this.providerRegistry = providerRegistry;
}
// Or using Components
public void myCustomMethod() {
this.providerRegistry = Components.getComponent(AssetProviderRegistry.class);
}DAM templating functions
As a template developer, have a look at damfn, a set of methods that can be used in FreeMarker scripts to easily access assets, asset renditions, and so on.