My first content app
My first content app
Tutorial overview
The tutorial consists of three parts:
Going through the tutorial you learn:
-
How to define content types and use them to quickly create a content app.
-
The basics of configuring fields and setting field validators.
-
How to override configuration properties.
-
How to make the elements of the app’s UI ready for internationalization.
|
If you want to skip the tutorial and install the final app immediately, clone the repository containing the ready-made Bookshelf app as a light module directly into your Magnolia light module folder with the command: |
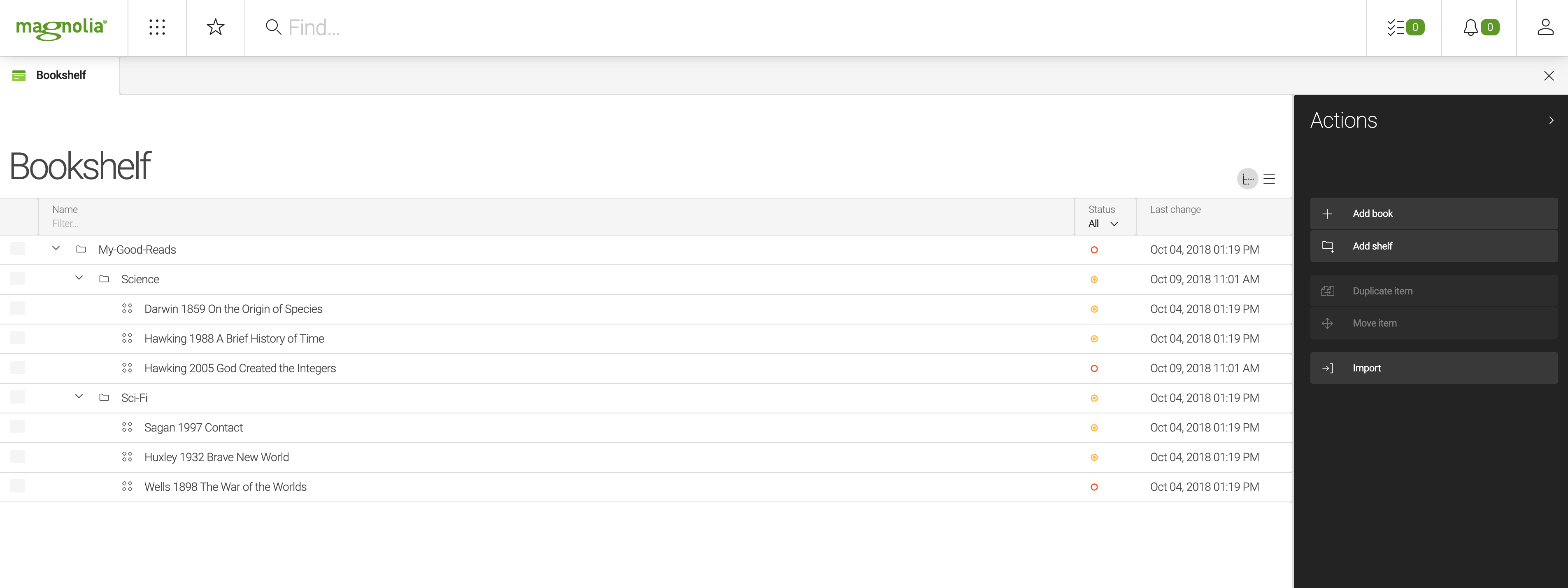
Bookshelf app use case
The Bookshelf app you create in this tutorial is an example of a content app. It is a simple book catalog allowing the user to store bibliographic data about each book: its title, the names of the author(s), the publisher’s name and the ISBN-13 number. The app also allows you to group selected book items into folders called shelves in the app.
Content app
A Content app is a specialized app type for managing structured content. The content app user interface consists of a browser subapp and one or more detail subapps. Content apps make it easy to enter items such as products or events. Many native Magnolia apps such as Tours and Contacts are content apps. Because this app style is used often, the framework provides convenience classes to make building a content app faster.
Bookshelf app subapps
The Bookshelf app consists of two subapps:
Book properties
For each book item, the Bookshelf app can store and retrieve the following content properties:
-
Short cataloging name (a required content property).
-
Full book title.
-
Author(s)’ name(s).
-
Whether the author(s) role is editorial or not.
-
Book description.
-
Publisher’s name.
-
Book publication date.
-
ISBN-13 number.
Bookshelf app and Magnolia content types
The Bookshelf app is based on Magnolia content types.
| See the following subsections for more details about the app’s design parameters. |
The books workspace
Magnolia stores content in the magnolia repository, a JCR repository that is divided into workspaces. The Bookshelf app is to store all books in a new workspace called books.
Custom lib:book node type
In the books workspace, each book is a custom lib:book node type defined for this tutorial.
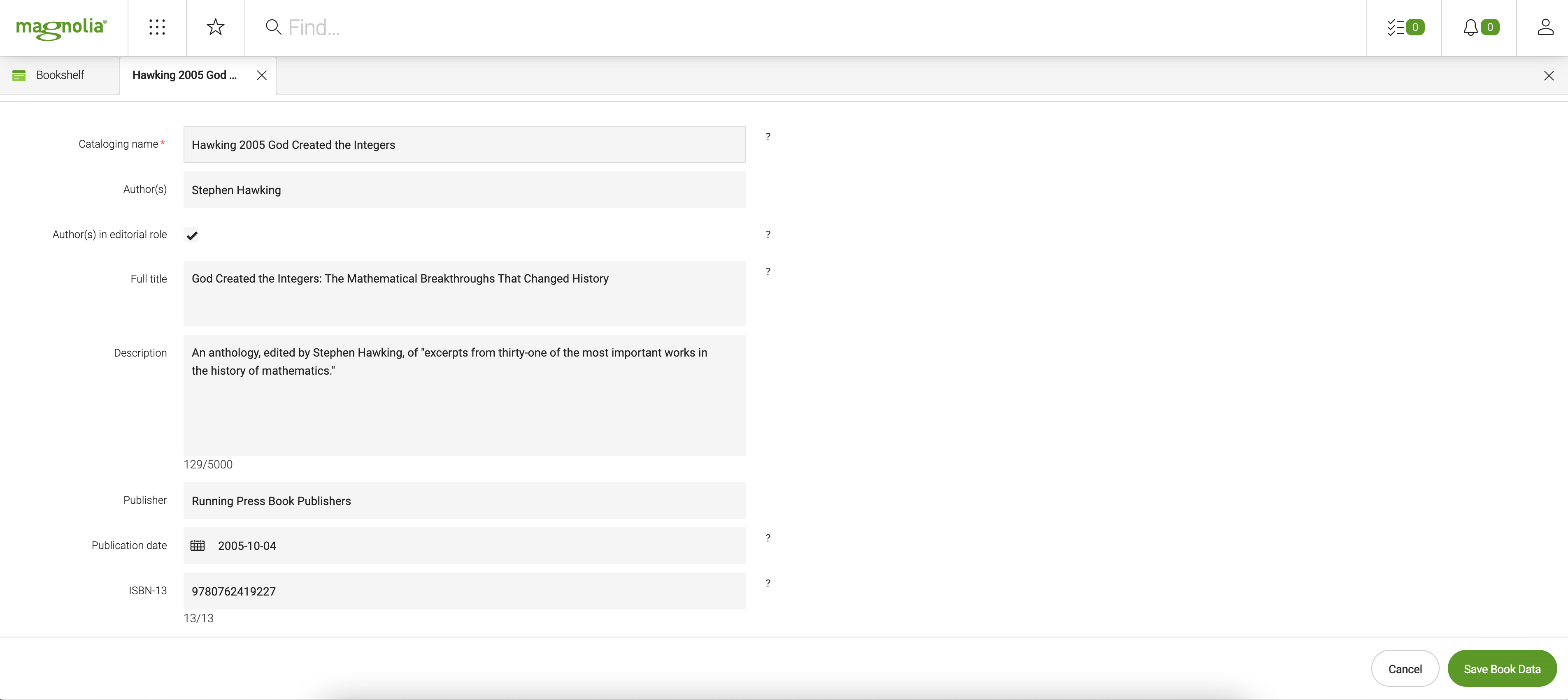
Content properties
Each book of the lib:book type can have the following content properties:
| Property | Usage | Type | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Name(s) of the author(s) of the book. |
String |
none |
|
The property to store the |
Boolean |
none |
|
Official book title. |
String |
none |
|
Description of what the book is about. |
String |
5000 characters max. |
|
Book publisher’s name. |
String |
none |
|
Date of publication of the book. |
Date |
Display format:
|
|
International Standard Book Number in the 13-character variant. |
String |
13 characters
|
The name property
When you create an app from a content type definition, the name property is generated automatically. Then the JCR node name is automatically deduced from the name.
We make use of this auto-generated name property in the Bookshelf app by:
-
Setting it to be a required property.
-
Referring to it via the Cataloging name label in user dialogs.
-
Using it for creating a short and hyphenated book identifier (JCR node name) such as:
Hawking-2005-God-Created-the-IntegersTherefore, in the Bookshelf app, the data in the Cataloging name field must be entered using the following syntax:
<first-author's-surname> <publication-year> <short-form-of-the-book's-full-title>For example:
Hawking 2005 God Created the IntegersMagnolia automatically replaces the spaces with hyphens when creating a node name from the
nameproperty.