App framework
The app framework is a name for Magnolia functionality that deals with apps. It also controls app lifecycle events such as starting and stopping and bringing the app into focus.
Adding subapps
As an app developer you will use the app framework to create new subapps. The subapp receives callbacks from the framework regarding location changes. A location change can occur for example when a user requests a URL that has a history fragment or when the user does something that requires the app to react with a new location. An example of the latter is when the user clicks Edit page in the Pages app. This requires a new detail subapp to be opened and brought into focus. The framework dispatches the location to the correct app, in this case to the parent app Pages. Think of the app framework as the master that gives instructions to slave subapps.
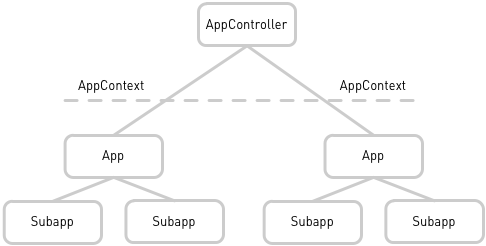
Managing context with the AppController
The AppController manages a context for each running app and exposes an
AppContext object to the app. An app uses the AppContext to interact
with the app framework. The AppContext is available for injection
anywhere in an app. Interacting with the AppController directly isn’t
necessary.
You can use AppContext to open new subapps and bring them to
fullscreen mode. The AppContext to send messages to the current user
or all users and display confirmation dialogs. The methods provided by
the AppContext are convenient because you don’t have to search for the
manager responsible for messaging. Here are some example methods:
-
openSubApp -
openSubAppFullScreen -
sendUserMessage -
showConfirmationMessage -
setSubAppLocation
Each app needs to implement the App interface. The Magnolia Shell
calls the App interface when the user interacts with the app. The
subapp represents a view open in a tab within the app.
The location is routed down the tree as app:<appName>:<subAppId> for
example app:pages:detail;/travel/about
What happens on a location change?
When a location changes, this is what happens in the app framework:
-
If the location starts with
appit gets passed to the app framework. -
The app framework looks at the next part, the app name, and starts that app if it is not yet running.
-
The next piece of the location it looks at is the
subAppId.-
If there’s a subapp running with this ID it calls the
locationChangedmethod on it, passing the whole location. This allows the subapp to react to any additional parameters in the location. -
Otherwise, it calls the app,
locationChangedallowing the app to open a new sub app.
-